|
|
Jordan Creek Center 8800 Glacier Hwy., Suite 236 Juneau, Alaska 99801 907.790.4880 |
|||
|
||||

|
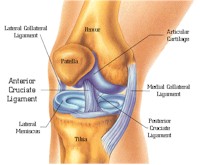
The Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) The ACL is one of four major knee ligaments that are susceptible to injury. The ACL helps to provide knee stability with daily activities such as walking, as well as recreational activities such as skiing and volleyball. ACL reconstruction Your ACL may need to be surgically reconstructed after injury. A variety of surgical methods may be used by your orthopedic physician to meet your needs. Physical therapy following ACL reconstruction
Also See:
The Rotator Cuff Four muscles in your shoulder, collectively termed the "rotator cuff", provide stability to your shoulder. These muscles are prone to tears and strains, especially if you overuse your arm, have poor posture, or have muscle tightness and/or weakness. How do you know if you have a rotator cuff injury? Injury may be sudden, i.e. the result of trauma, or come on more slowly. Pain most often is located on the outside of your upper arm or in your shoulder. Overhead reaching activities are commonly painful. Why see a Physical Therapist? Your physical therapist will perform an evaluation including the identification of strength deficits, tightness, and poor posture. After identifying factors that may be contributing to your symptoms, we will then design a program to help alleviate the sources of the problem. Rotator Cuff Surgery Rotator cuff surgical repair will differ with each individual. Rehabilitation after surgery often includes extensive stretching followed by the initiation of a strengthening program at the appropriate time post surgery as indicated by your physician. Modalities such as heat, ice, and ultrasound may be used to decrease discomfort and facilitate recovery If you have leg and/or foot pain, answer the following questions. If you have answered "yes" to any of the above questions, you may have identified one or more causes of your leg or foot pain. What can physical therapy do? Our physical therapists will identify factors that may be contributing to your pain. We will then design a program to alleviate the sources of the problem. Your physical therapy program may include treatments such as exercises to improve your strength and flexibility, fitting for orthotics, thermal modalities such as heat and ice, joint mobilization, and education to help you modify or eliminate aggravating activities. Can an ankle injury cause back pain? Did you know that structural faults or muscular imbalances at the ankle can effect other joints such as the knee, hip, or even your back? Conversely, an injury to the back might effect the joints down below. Your physical therapist will examine other symptomatic areas to determine if one or more causes of your pain exist. Why do you have back and neck pain in pregnancy? Pregnancy is a natural physiological process that is accompanied by factors that cause many changes in your body. Fluctuations in hormone levels create laxity within the joints and muscles. The additional weight of your baby causes a shift in your center of gravity. These factors can lead to poor posture and may be associated with neck and low back pain. In addition, poor pelvic alignment, a common result of increased joint laxity with pregnancy, may result in low back pain. Why see a physical therapist? A physical therapist can provide instruction on safe and easy exercises to help maintain good posture and an adequate level of fitness. This includes strengthening of the abdominal and low back muscles which assist in developing correct postures. Heat, ice, and massage may be used to help decrease aggravating symptoms. Pelvic floor exercises are taught to help you maintain and improve your muscle tone in order to prevent the common occurrence of stress incontinence. Varicose veins Varicose veins sometimes occur with pregnancy. Your physical therapist is trained to fit you for support stockings to help minimize varicose veins. What is the TMJ? The TMJ is the joint where your jaw bone meets your skull in front of your ears. What causes TMJ pain? Symptoms produced by TMJ dysfunction can include jaw pain, headaches, neck pain, ear discomfort, and facial soreness. In many cases, these symptoms can be resolved by reeducating your muscles to function properly, correcting poor postural habits, eliminating stressful habits like ice and gum chewing, and learning how to relax and rest your jaw in a proper position. Should I attend physical therapy? If your symptoms match the ones listed above, you may be a candidate for physical therapy. You may also be a candidate for physical therapy if you use a night guard or have had a dentist suggest one due to teeth grinding. Lastly, constant teeth clenching puts you at risk for developing TMJ problems. Treatment is most effective if it is begun as early as possible. If left untreated for too long, actual damage may be done to the structures that make up the TMJ. Commonly after a few therapy sessions you will have the information you need to continue your treatment on your own. What is incontinence? Incontinence or the loss of bladder control affects 12 million Americans. This condition is a troublesome and embarrassing problem that warrants treatment. Unfortunately, more than half of the people who experience incontinence do not seek medical help. Types of incontinence Stress Incontinence People with stress incontinence lose urine when they exercise or move in a certain way that places stress on the bladder. If you have stress incontinence, you may leak urine when you sneeze, cough, laugh, get up from a chair, get out of bed, or when you walk or do other exercise. You may also go to the bathroom often during the day to avoid accidents. Urge Incontinence People with urge incontinence lose urine as soon as they feel a strong need to go to the bathroom. If you have urge incontinence you may leak urine when you canít get to the bathroom quickly enough, when you drink even a small amount of liquid, or when you hear or touch running water. You may also go to the bathroom very often; for example, every two hours during the day or night. You may even wet the bed. Overflow incontinence People with overflow incontinence may feel that they never completely empty their bladder. If you have overflow incontinence, you may often experience one or more of the following: loss of small amounts of urine during the day and night, getting up often during the night to go to the bathroom, feeling as if you have to empty your bladder but canít, passing only a small amount of urine but feel as if your bladder is still partly full, or spending a long time at the toilet but producing only a weak, dribbling stream of urine. Some people with overflow incontinence do not have the feeling of fullness, but they lose urine day and night. How can physical therapy help? At Action Rehab our goal is to help you improve your bladder control through exercise instruction (Kegels), behavioral treatment (i.e. modifying how frequently you urinate), and biofeedback therapy if necessary. What is a Kegel? A Kegel is a contraction of the muscles of your pelvic floor which support your bladder and help to control your urine output. Many women suffering from stress incontinence have been told to perform Kegels but have not been given any formal instruction. The result has been that many women may be performing these exercises incorrectly. One study found that in one group, 80% of the women were performing Kegels improperly. Biofeedback can be used along with instruction in Kegel exercises to monitor how well you are actually performing the exercise. One form of biofeedback measures pressure to give information about how well the exercise is being performed. Seek help No matter what the cause of your incontinence, you can become more actively involved in your health care. Donít let this condition limit your enjoyment of life. Also See: Posture is defined as the position we allow our body parts to rest in when we are sitting or standing. On the other hand, body mechanics is the way we stabilize and move our body when we are lifting or carrying objects. Poor posture and inappropriate body mechanics can contribute to a variety of injuries including back and shoulder pain. Often people are not aware that they are aggravating an injury when they sit or stand with poor posture or move incorrectly. Proper Posture The spine and soft tissue structures that surround it are best protected when an appropriate posture is assumed. This attitude of the body is also known as the "neutral spine" position, in which oneís shoulders are held in line with the ears and a gentle curve is maintained in the low back. The neutral spine position is the safest position for the muscles to accept weight loads. Body Mechanics Good body mechanics begins with an understanding of how to maintain good posture in a stationary position. The next step is to learn to move your body while maintaining this correct posture in order to minimize the strain placed on joints and soft tissue structures. The use of good body mechanics is essential when lifting. How can physical therapy help? Your physical therapist can help you determine if poor body positioning is contributing to your current physical condition. The therapist can then provide instruction to help you to achieve and maintain good posture with various functional activities, particularly lifting. Donít be fooled into thinking you always lift with good body mechanics. Unfortunately, a lot of people who believe they lift properly donít quite have it right. It is also important to ALWAYS lift with good body mechanics. Even the lifting of light items repetitiously can, over time, cause injuries. Neck and back pain can make even the most simple daily functions uncomfortable. In most cases, an individual with back or neck pain has the power to improve this condition through physical means. These means include heeding to appropriate posture and body mechanics instructions and completing an individualized exercise program. Why Physical Therapy? The general public is often unaware of how physical therapy can address back and neck pain. As back and neck pain can result from many causes, the first job of your therapist is to determine possible physical factors contributing to your condition.
Your physical therapist will examine factors such as those listed above that may be contributing to your symptoms. Then he or she will design a specific program for you to help alleviate the sources of the problem. Our goal is to decrease your pain, improve your ability to function, and provide you the knowledge to treat your neck or back independently in the future. Do you ever feel an increase in pain in a muscle or joint when you are experiencing stress? What is stress? Stress is the mental, emotional, and physical strains that are placed on us daily. Both positive and negative stresses occur in daily life. An example of a positive stress is preparing for a vacation; you are excited and happy to be going on vacation, but you must plan your events, pack, arrange a dog-sitter, etc. before you can go. Just the preparation places a strain on you and can influence your body adversely. One manifestation of stress is an increase in muscle tension. How can physical therapy decrease my stress? Physical therapists often treat individuals who are experiencing muscle tension and pain that is associated with stress. Commonly a patient is not aware that stress may be a primary contributor to his or her discomfort, such as in the cases of neck or back pain. If the patient can be made aware of his or her sources of stress and the affect it has on the body, then it can be controlled. Controlling stress may in turn produce a reduction in oneís pain. Your physical therapist can provide you with instruction to help you get started in managing your stress. Physical therapists utilize stress reduction exercises and visualization techniques to provide patients with tools to alleviate stress. Another tool that a physical therapist may employ to help you reduce stress is biofeedback. Biofeedback is simply the use of machinery to provide you with an indirect measure of your level of stress. For example, imagine that after a stressful day at work you find the muscles behind your neck are tense and painful. A biofeedback machine is used to provide you with instant feedback regarding the level of activity in the muscles of your neck. If you are getting more tense in your neck, you will receive feedback through light and/or sound indicating increased muscle tension. If you are relaxing, the lights and/or sound will dim in proportion to the decrease in muscle activity. This feedback, along with additional techniques used by your physical therapist such as mental imagery, aims to increase your awareness of tension in a specific part of your body. Our goal is to help you to be able to relax your body when you feel stress building before pain begins. What is carpal tunnel syndrome? Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is the term used to describe a condition that is thought by many to involve the compression of the median nerve at the wrist. The median nerve runs though a tunnel formed by the wrist bones on the palm surface of your wrist. Symptoms of CTS may include numbness, tingling and/or pain in your thumb, index, middle and ring finger. Pain may also be felt in the wrist, forearm, or upper arm. It is possible that an injury to another area of your body, such as your neck or shoulder, may cause similar symptoms. What causes carpal tunnel syndrome? Activities requiring repetitive wrist movement such as typing or writing may result in CTS. In addition, CTS may be caused by a job that requires a high level of force to be generated at the wrist, or a traumatic injury to the wrist such as a fracture. Why see a physical therapist? Your physical therapist will perform an examination that includes the identification of physical limitations such as wrist tightness or weakness that may be affecting your median nerve. Your therapist will use this information to design a program for you to help alleviate your symptoms. In addition, your therapist will help you identify activities that are aggravating your condition and make suggestions regarding how to modify these activities in order to decrease nerve irritation. What is ergonomics? Ergonomics is the science that studies the problems of people in adjusting to their environment, especially seeking to adapt work or working conditions to suit the worker (Websterís New World Dictionary). In other words, ergonomics answers questions such as "does your computer workstation fit the needs of a person of your bodily characteristics (i.e. height)? How can you alter your workstation so that you are able to perform all work or leisure related computer activities while maintaining proper posture?" Ergonomic principles can be applied to any profession whether sedentary or active. In addition, ergonomic principles should not be limited to the work setting. Understanding the principles allows you to apply the same concepts to leisure time activities. For example, activities such as chopping wood, quilting, fine woodworking or needle crafts can be adjusted to reduce the strain on your body. Can ergonomics help reduce my pain? Improper postures, using ill-fitting equipment while completing excessive repetitions, or using excessive force, can all lead to cumulative trauma on your body. Applying ergonomic principles to all your activities can protect you from this type of injury. If you already have an injury present, changing your environment to reduce bodily stress is essential in order to aid the healing process and prevent re-injury. How can my physical therapist help? What is a work site assessment? This assessment occurs when your physical therapist visits your workplace to evaluate how your workstation is affecting your physical condition. The visit allows your therapist to most accurately suggest changes that will benefit you. How will my hand work after an injury? After an injury to your hand or wrist, such as a fracture or sprain, you hand may not be the same as the opposite hand and wrist. The injured hand may demonstrate swelling, muscular weakness, limited mobility, and difficulty gripping and carrying objects like a coffee cup or gallon of milk. What can physical therapy do? During your treatment sessions, a physical therapist may use thermal modalities to decrease your pain and swelling. He or she may also perform small movements at the individual joints of your hand to increase your overall wrist movement. In addition, you will be educated on exercises to help you regain motion and strength in order to return you to your daily activities as soon as possible. What causes headaches? Tension headaches are usually felt at the base of your head and can radiate across the top and side of your head. They may be caused by one or more of the following factors:
These factors may lead to a sustained muscle contraction in the neck, which causes a decrease in local blood flow and results in pain. Other causes of headaches include migraine, allergy, or sinusitis. |
|||||||||||
| [ Top of Page ]
[ Home ] [ Why
See a PT ] [ What
We Do ] [ See
a PT ] [ What We Treat ] [ PT Month ] [ Links ] Copyright ©1999, Action Rehab LLC. All rights reserved. |
||||||||||||